
The reduction of solar energy by the atmosphere is shown by the Air Mass (AM) parameter denoted by AM=1/cosΘ. In outer space we can expect to receive a full blackbody spectrum from the sun, but on the ground the solar energy received is really depend on its location. Solar energy could also be used to power satelites and outer space vehicles. Theoretically the more subcells put into, the more electricity produced by the solar cells. Recently some groups have claimed to approach or even surpass 40% solar cells efficiency. Multijunction solar cells use several semiconducting layers or subcells, each with different bandgap energy and absorption coefficient. The development of high efficiency solar cells mostly focused on multijunction solar cells made from III-V compounds like GaAs, AlGaAs, InP, and GaInP. One way to reduce the need for this massive area is by inventing a new type of solar cells with a high efficiency rate.

As an example the largest solar farm in the world, Topaz solar farm in California, can produce electricity up to 550 MW and power almost 200,000 homes, but it takes about 25 km 2 area. With such a low efficiency a large area will be needed for installing a solar farm. Most of the solar cells available in the market are silicon based panels with efficiency up to 15%, while cheaper panels based on amorphous silicon can only produce half of it.
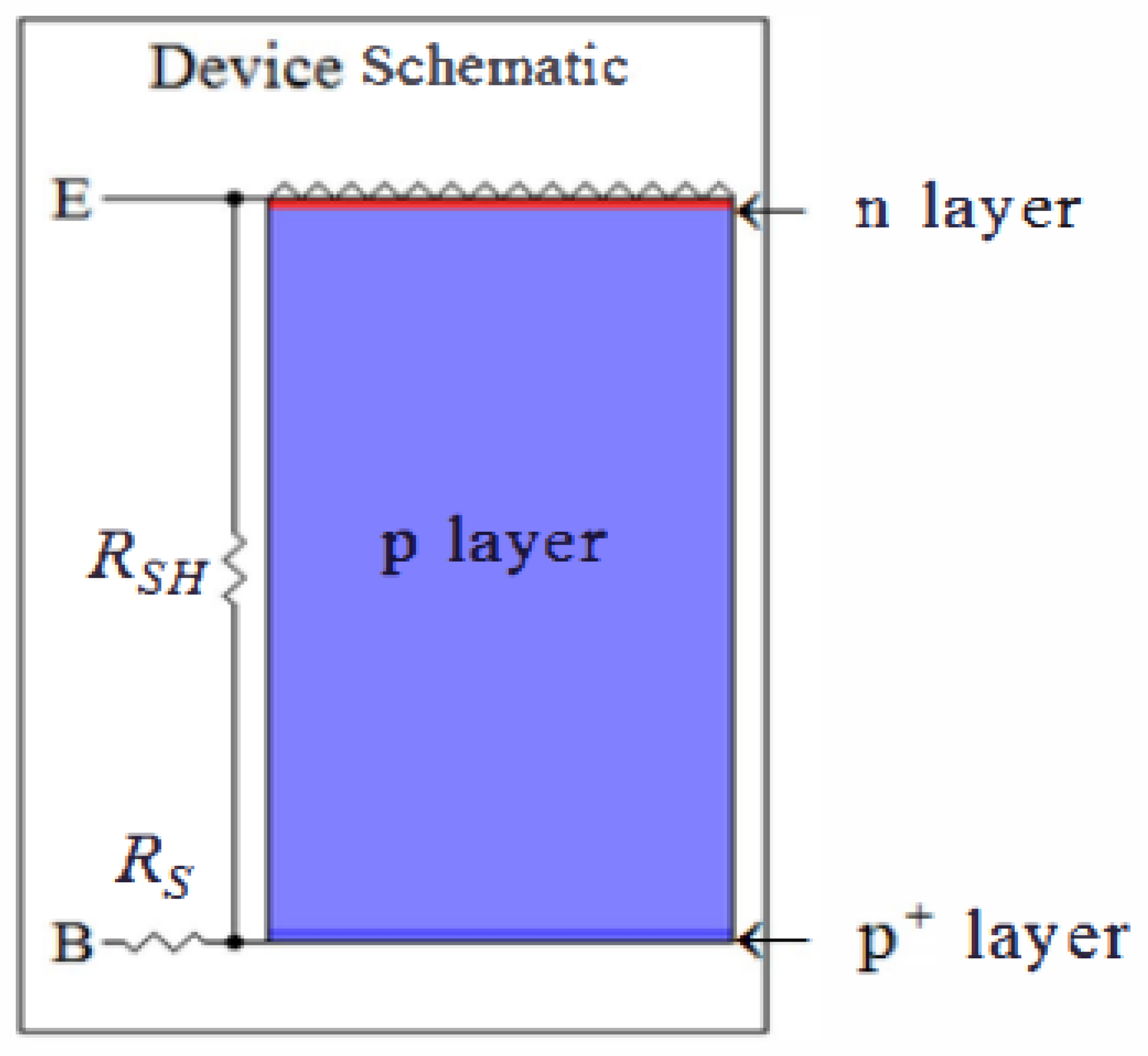
The abundance amount of solar energy and the zero emission produced are some of the reasons that motivate people to continue research in this field.
Solar energy is one of the most promising renewable energy resources in the world.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
